I. Why Maritime Chokepoints Are the Real Pressure Points of Global Power

While missile technology and cyber warfare grab headlines, control of the sea lanes remains one of the most decisive levers in geopolitics. Over 80% of world trade by volume moves by sea, and much of it passes through a handful of narrow straits and canals.
Choke off one of these routes, and you can:
- Cripple rival economies in weeks
- Disrupt global supply chains overnight
- Force military concessions without firing a shot
II. The Classic Chokepoints — and Their Vulnerabilities
1. Strait of Malacca
- Handles ~25% of all global trade, connecting the Indian and Pacific Oceans
- Narrowest point only 1.7 miles wide
- Vulnerable to piracy, naval mines, and submarine ambushes
- China’s “Malacca Dilemma” — almost 80% of its oil imports pass here
2. Strait of Hormuz

- Vital for ~20% of global oil supply
- Iran has repeatedly threatened closure during tensions
- Can be shut down with small, fast missile boats and layered minefields
3. Suez Canal
- Shortcut between Europe and Asia — closure adds ~10 days of sailing
- Ever Given blockage in 2021 showed how fragile the route is
- Strategic for both trade and naval mobility
III. The New Chokepoints Emerging in the 21st Century
1. Bab el-Mandeb
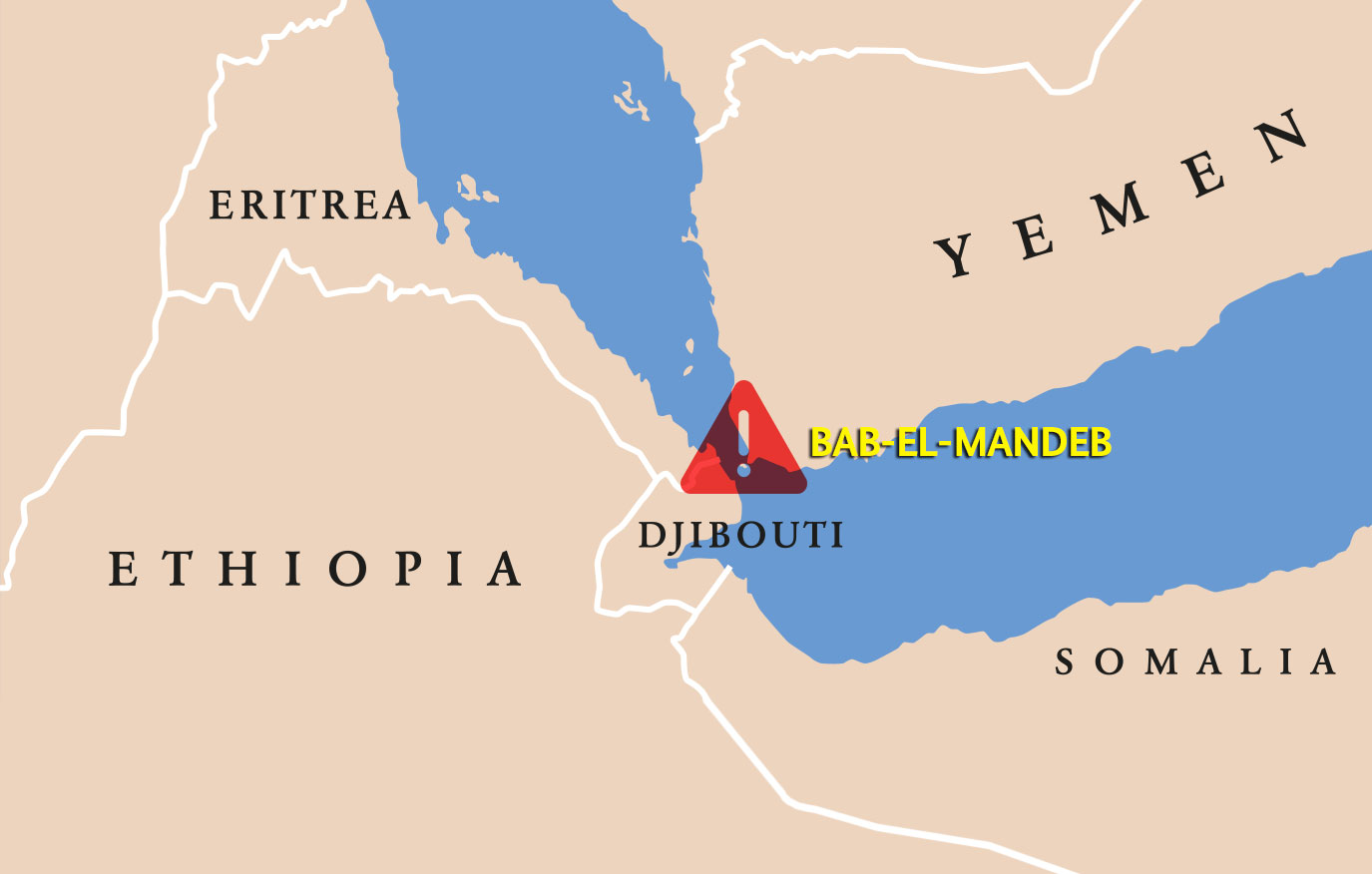
- Controls access between the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden
- Increasingly targeted by Houthi missile and drone strikes
- Threatens all shipping heading toward the Suez Canal
2. Panama Canal (and Potential Alternatives)
- Handles ~6% of global maritime trade
- Vulnerable to climate impacts (drought already limiting ship transits)
- Chinese-backed Nicaragua Canal plans could shift control dynamics
3. Arctic Sea Lanes
- Melting ice opens shorter shipping between Europe and Asia
- Russia militarizing the Northern Sea Route with missile bases and icebreakers
- Future conflict zone between NATO, Russia, and China
4. Subsea Infrastructure Chokepoints
- Undersea cables and pipelines often pass through narrow maritime corridors
- Sabotage (like the Nord Stream incident) can cripple economies without touching ships
IV. How Chokepoints Are Weaponized in Modern Strategy

- Naval Blockade — Traditional interdiction of merchant shipping
- Mine Warfare — Cheap, persistent threat to deter transit
- Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) — Using missiles, aircraft, and drones to make passage too risky
- Legal Warfare — Declaring “security zones” under the guise of anti-piracy or environmental protection to control shipping
- Hybrid Disruption — Cyberattacks on port systems, GPS spoofing of vessels, or targeted attacks on shipping insurance
V. Strategic Recommendations for Nations
- Diversify Trade Routes: Invest in overland rail corridors to reduce maritime dependence
- Chokepoint Bypass Projects: Pipelines, alternate canals, and new port infrastructure
- Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA): Deploy satellites, drones, and sensor networks to monitor shipping lanes in real time
- Covert Capability: Maintain mine-laying submarines, drone swarms, and legal maritime claims as deterrence tools
- Coalition Naval Patrols: Joint task forces to secure vulnerable routes (like Operation Sentinel in Hormuz)
VI. The Future: Chokepoints in 2035
Expect to see:
- Privatized Chokepoint Security — shipping companies hiring their own armed escort drones
- AI Port Sabotage — cyber tools designed to cause cascading container misplacements and trade chaos
- Arctic Militarization — a race to fortify northern shipping corridors
- Insurance Warfare — states making shipping so risky that insurers refuse coverage, effectively halting trade








![ANALYSIS] TCG Anadolu: the most powerful warship and the flagship of the Turkish Navy - Turkish Minute](https://www.turkishminute.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/tcg-anadolu.jpg)

